Increased numbers of preterm births, higher incidence of respiratory disease and death, and more children in hospitals are some of the stark health outcomes the world is facing from the impacts of extreme climate change. This morbid reality will devastate children’s health for generations without global action.

Scientists have spent decades warning the world about the risks of extreme temperatures, floods, and bushfires, but our new study published in Science of the Total Environment is the first to collect all the available scientific evidence for the effects of climate change on children’s health.
Led by Lewis ‘Darth’ Weeda of the University of Western Australia, we did a systematic review and meta-analysis to identify which particular climate-driven extremes are linked to certain detrimental health impacts for future generations.
The global data have revealed a worrying increase in preterm birth rates that could cause lifelong complications for millions of children around the world.
We identified many direct links between climate change and child health, the strongest of which was a 60% increased risk on average of preterm birth from exposure to temperature extremes. Respiratory diseases, mortality, and morbidity, among others, were also made worse by climate change.
The effects of different air pollutants on children’s health outcomes were smaller compared to temperature effects, but most pollutants still had an effect of some type, so the news is concerning. The children’s health issues we identified depend on weather extremes — cold extremes give rise to respiratory diseases, while drought and extreme rainfall can result in stunted growth for a population.
Most of the analysed studies were in high-income nations, despite the fact that children in lower-income countries are most likely to go without adequate access to healthcare, infrastructure, and stable food supply.
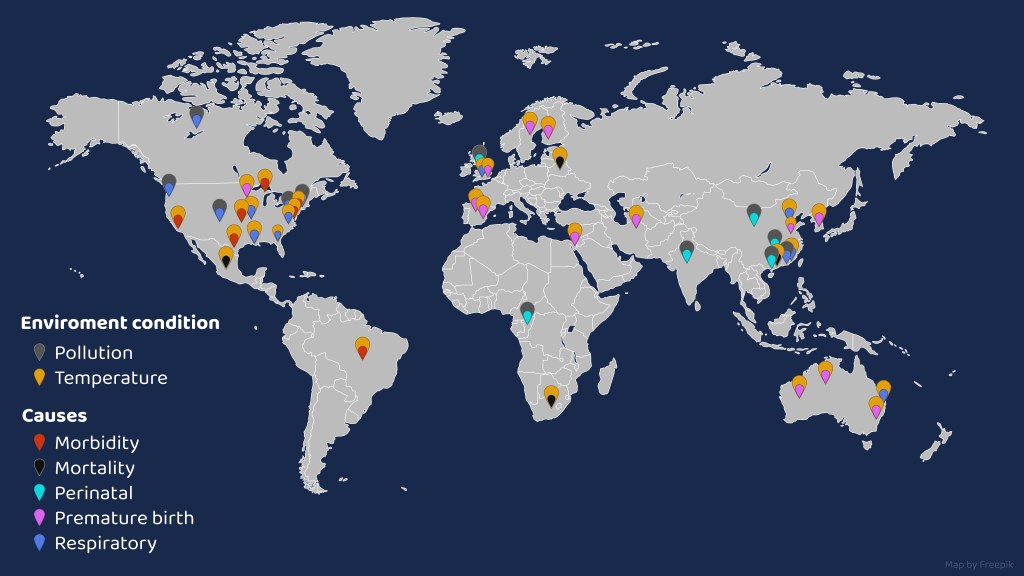
Our research also revealed that even advanced economies will not avoid the impacts of climate change on children’s health, even though health risks vary across continents and depend on socio-economic circumstances.
Given that climate influences childhood disease, social and financial costs will continue to rise as climate change progresses, placing increasing pressure on families and health services. For example, asthma has been estimated to cost as much as US$1.5 billion due to a single fire season in the future, while another study estimated the costs of a single case of childhood asthma at up to US$23,573 in the coming years.
Geography also dictated the health impacts of climate change. For example, in Australia, extreme temperatures have led to an increase in premature births on the east coast, Northern Territory, and Western Australia and enhanced respiratory issues in Queensland, while similar temperatures have caused higher mortality rates in South Africa.
Action is required to protect children from climate-related disease. Our research recognises some important areas where children are most vulnerable to climate change. The development of public health policies to counter these climate-related diseases, alongside efforts to reduce anthropogenic climate change, must be addressed if we are to protect current and future children
Finding solutions and implementing climate adaptation and mitigation policies would positively impact multiple United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Climate change is universal and adversely affecting all countries and people, and we must prepare societies for mounting threats to child health.
Read the detailed, open-access study here. Supported by Population Matters.


